CHRONIC STRESS: AN OVERVIEW OF ITS SYMPTOMS AND FACT SHEET
Stress is a natural and normal part of our modern lives. In moderate amounts, stress can motivate us to meet deadlines, solve problems efficiently, and handle challenging situations. This type of stress, known as acute stress, is typically short-lived and resolves once the immediate pressure or threat has passed. However, when stress becomes chronic—persisting over weeks, months, or even years—it can have serious consequences for both physical and mental health. Chronic stress can lead to a range of health issues, including cardiovascular problems, weakened immune function, and mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression.
Below, we explore some of the common symptoms associated with chronic stress, highlighting how this prolonged state of tension can affect nearly every aspect of life.
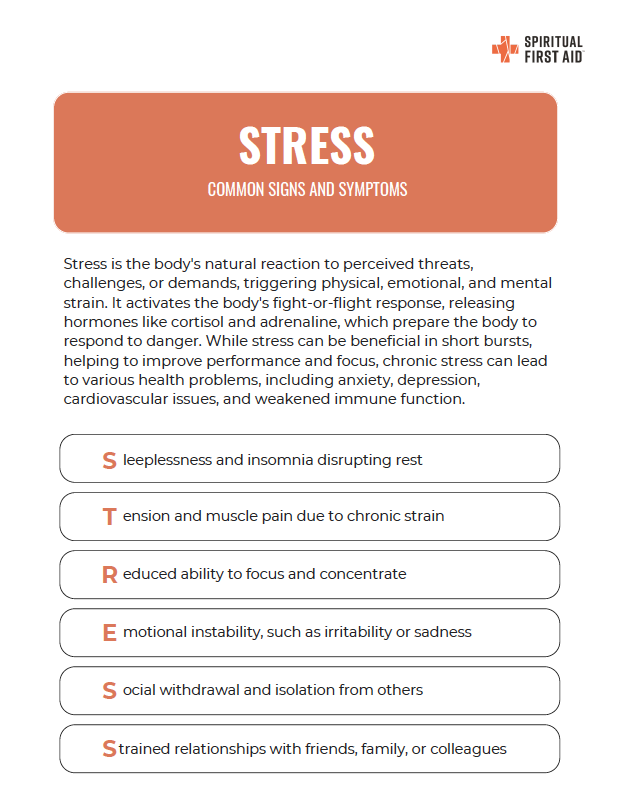
Sleeplessness and Insomnia Disrupting Rest
One of the most prevalent symptoms of chronic stress is disrupted sleep, which can manifest as difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing restless, non-refreshing sleep. Stress often keeps the mind racing with worries and concerns, preventing the body from entering a restful state. Over time, this lack of quality sleep can lead to insomnia, further exacerbating stress and leading to a vicious cycle of exhaustion and anxiety. Chronic sleeplessness not only impacts energy levels but can also impair cognitive function, emotional regulation, and overall well-being.
Tension and Muscle Pain Due to Chronic Strain
Chronic stress often manifests physically as muscle tension and pain. When the body is under prolonged stress, it remains in a constant state of readiness, leading to tight muscles, particularly in the neck, shoulders, and back. This prolonged strain can result in headaches, tension-related back pain, and even conditions like temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders. Over time, this physical toll can become chronic pain, further diminishing a person’s quality of life and adding to their stress.
Reduced Ability to Focus and Concentrate
One of the cognitive symptoms of chronic stress is a reduced ability to focus and concentrate. When stress overwhelms the mind, it becomes increasingly difficult to focus on tasks, make decisions, or process information effectively. This mental fog can lead to decreased productivity at work or school, and may also affect daily tasks, such as remembering appointments or following through on responsibilities. Over time, this cognitive decline can lead to frustration and a sense of incompetence, adding to the emotional burden of stress.
Emotional Instability: Irritability and Sadness
Chronic stress significantly impacts emotional well-being, often leading to emotional instability. Individuals under prolonged stress may experience mood swings, irritability, or sudden outbursts of anger. They may also feel overwhelmed by sadness, helplessness, or a sense of hopelessness. These emotional responses are often disproportionate to the immediate situation, as the accumulated effects of stress heighten sensitivity to daily challenges. Over time, this emotional instability can contribute to the development of anxiety, depression, or other mental health issues.
Social Withdrawal and Isolation from Others
Another common symptom of chronic stress is social withdrawal. When overwhelmed by stress, individuals may begin to pull away from social interactions, choosing isolation over engaging with friends, family, or colleagues. This withdrawal can stem from feelings of exhaustion, irritability, or simply feeling too overwhelmed to connect with others. While isolation might seem like a way to conserve energy, it often leads to increased loneliness and can further contribute to feelings of sadness or despair.
Strained Relationships with Family, Friends, or Colleagues
Chronic stress can also place a significant strain on relationships with family, friends, and colleagues. Strained relationships often result from increased irritability, emotional outbursts, or withdrawal from social interactions. Misunderstandings may arise, leading to conflict or distancing in relationships. The individual under stress may feel misunderstood or unsupported, while loved ones may struggle to know how to help or may feel hurt by the person’s behavior. Over time, these strained relationships can contribute to a sense of isolation and exacerbate the stress even further.
Chronic stress is more than just a prolonged feeling of pressure; it’s a serious condition that can affect nearly every aspect of life. From disrupted sleep and physical pain to emotional instability and strained relationships, the effects of chronic stress can be overwhelming. Seeking support through therapy, stress management techniques, and self-care practices can help individuals regain control over their lives and reduce the long-term impact of chronic stress on their health and well-being.
As a reminder, God invites us to cast our burdens on Him. In Matthew 11:28, Jesus says, “Come to me, all you who are weary and burdened, and I will give you rest.” Recognizing the symptoms of chronic stress is the first step in seeking healing, both physically and spiritually. Laying our burdens on Christ, finding true rest in Him, and leaning on the support of a faith community, we can find peace amidst the pressures of life. By placing our trust in God and practicing self-care, we can work towards restoring balance and finding rest for our souls, even in the face of life’s challenges.
Check out the Spiritual First Aid Fact Sheet below regarding Chronic Stress for quick reference.
Enjoyed our blogpost? Subscribe to our newsletter for more resources on mental health and integrating the Gospel message in your healing journey.
If you found our resources useful, please consider donating to Oak Health Foundation, which is a 501(3)c nonprofit dedicated to providing resources regarding holistic mental healthcare and subsidized treatment for those in need.